23+ Do Plants Have Cytoskeleton
Web The plant cytoskeleton composed of microtubules and actin filaments is a highly dynamic structure in cells and participates in many physiological activities for instance material transport organelle movement and cell division. The cytoskeleton plays an important part in eukaryotic organisms.

Do Plant Cells Have Cytoskeleton Functions Structure The Gardeners World
Just like animals plants also contain a cytoskeleton.

. The eukaryotic cytoskeleton is a dynamic filamentous network with various cellular and developmental functions. Web 2023 Khan Academy Terms of use Privacy Policy Cookie Notice. Web Part of the Plant Cell Monographs book series CELLMONOvolume 23 Abstract.
Web Recently research has demonstrated that the plant cytoskeleton undergoes rapid remodeling upon sensing pathogen attacks coordinating the formation of microdomain immune complexes the dynamic and turnover of pattern-recognizing receptors PRRs the movement and aggregation of organelles and the transportation of defense compounds. Plant cells cytoskeleton differs from that of the animal cell in terms of the building block. In eukaryotes it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms.
The actin cytoskeleton plays an essential role in several biological processes in plants including cell division cell expansion organelle movement vesicle trafficking and the establishment of polar cell growth. The cytoskeleton is responsible for the architecture of the organisms. This gives the plant cell its unique rectangular shape.
Both plant and animal cells need a cytoskeleton for internal structure and support. Plant cells have a cell wall as well as a cell membrane. Web The Plant Cytoskeleton.
Animal and plant cells share common elements like plasma membranes cytoskeletons and mitochondria. Web By Arti Pandey. It exists in all eukaryotic cells except for bacteria.
Plant and animal cells have a cytoskeleton. Microtubules form structures like flagella which are tails that propel a cell forward. The cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell maintains the cells shape and is responsible for the locomotion of the cell itself and the movement of the various organelles within it.
Web Cytoskeletons are essential elements for cellular function and viability and constitute a system of filaments or fibers present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells with numerous functions such as maintenance of cell shape intracellular transport of vesicles and organelles cell division and cell signaling 1 2. Web Cytoskeleton exists in plant cells. However they differ in certain aspects.
Web In contrast animal cells have many smaller vacuoles. The cytoskeleton of plant cells originates greatly from cellulose while the animal cytoskeleton is mostly actin filaments. Web The cytoskeleton is a complex dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells including those of bacteria and archaea.
It is made up of organelles suspended in the gel-like cytosol the cytoskeleton and various chemicals. Plant cells display a singular architecture necessitating a structurally and functionally unique cytoskeleton and plant specific control mechanisms. Web Features that plant and animal cells share include the nucleus nucleolus cytosol and cytoplasm centrosome Golgi lysosome peroxisome secretory vesicle cell membrane mitochondria vacuole smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes and.
Web They have a network of filaments known as the cytoskeleton literally cell skeleton which not only supports the plasma membrane and gives the cell an overall shape but also aids in the correct positioning of organelles provides tracks for the transport of vesicles and in many cell types allows the cell to move. They are hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin. In plants the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane.
Web The plant cytoskeleton is the network of protein filaments microtubules and interconnecting filamentous bridges that give shape structure and organization to the cytoplasm of the plant cell. The cytoplasm comprises the contents of a cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope a structure to be discussed shortly. Web Do plant and animal cells have cytoskeleton.
Web The highly dynamic plant cytoskeleton including actin and microtubule networks can rapidly alter their organization stability and dynamics in response to internal and external stimuli which is considered vital for. Web Cytoskeleton a system of filaments or fibers that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Web Microtubules are the largest of the cytoskeletons fibers at about 23 nm.
In addition the cytoskeleton also acts as a regulator of plant tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses 7. Plants are eukaryotic organisms which means they have membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria lysosomes nucleus ribosomes etc. Web The plant cytoskeleton consisting of actin filaments and microtubules is a highly dynamic filamentous framework involved in plant growth development and stress responses.
Web The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development including such fundamental processes as cell division cell expansion and intracellular organization and motility Staiger 2000. These functions have been intensively investigated using single cell model systems. Web The plant cytoskeleton has crucial functions in a number of cellular processes that are essential for cell morphogenesis organogenesis and development.
Overview of animal and plant cells. Web The organization and dynamics of the plant cytoskeleton change in response to diverse developmental cues and external signals such as light cold and mechanical stress thus participating in plant adaptation to the environment. Web The basic structure of an animal cell entails a plasma membrane surrounding a dense cytoplasm containing the nucleus and all the other organelles including the cytoskeleton and the cytoplast is often coated with a thin extra-cellular matrix.
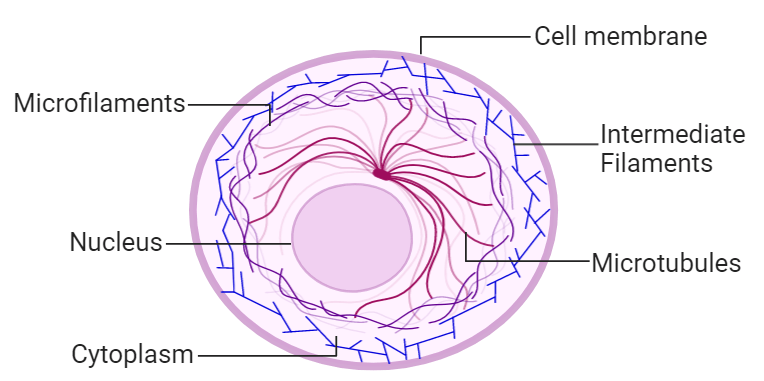
Cytoskeleton Javatpoint
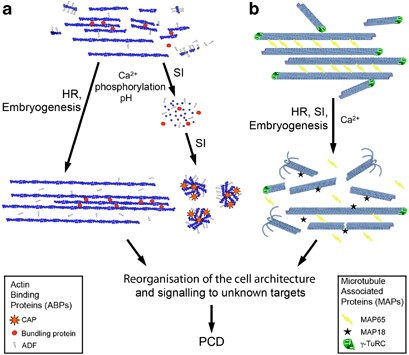
Organisation And Regulation Of The Cytoskeleton In Plant Programmed Cell Death Cell Death Differentiation

The Progressive Growth Of The Actin Cytoskeleton In Dendritic Spine Download Scientific Diagram

Do Plant Cells Have Cytoskeleton 5 Facts You Should Know
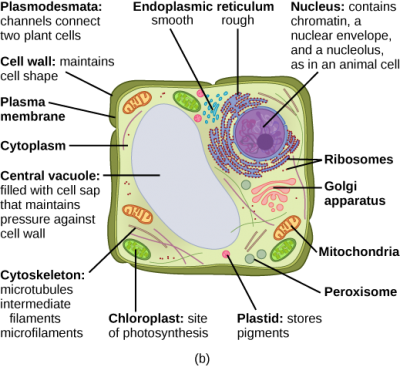
3 3 Eukaryotic Cells Biology And The Citizen

Which Structures Of The Cytoskeleton Are Found In Animal Cells But Not In Plant Cells Homework Study Com

S Kim Suvarna Mbbs B Sc Frcp Frcpath Auth S Kim Suvarna Eds Cardiac Pathology A Guide To Current Practice 2013 Pdf Heart Valve Atrium Heart
Do Plant Cells Have Cytoskeleton What Are Its Functions Quora
Plant Cytoskeleton Latest Research And News Nature

Loss Of Function Gene Leaders In Pharmaceutical Business Intelligence Lpbi Group
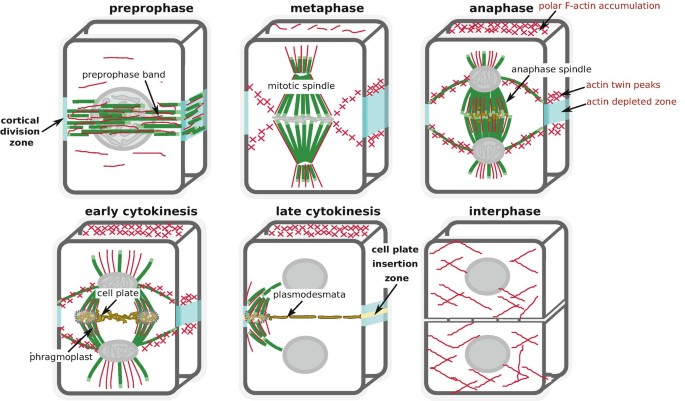
Methods To Visualize The Actin Cytoskeleton During Plant Cell Division Springerlink

Do Plant Cells Have Cytoskeleton Functions Structure The Gardeners World
Plant Cytoskeleton Latest Research And News Nature

Wnbzdsva4vwyxm
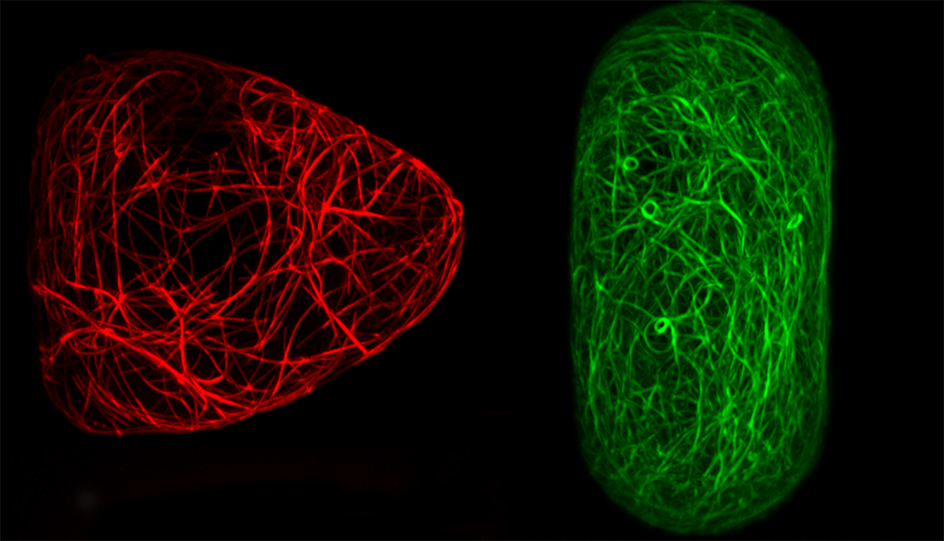
Cells In Tight Spaces How The Cytoskeleton Responds To Different Cell Geometries Sainsbury Laboratory

Pdf Stitching Together The Multiple Dimensions Of Autophagy Using Metabolomics And Transcriptomics Reveals Impacts On Metabolism Development And Plant Responses To The Environment In Arabidopsis

Do Plant Cells Have Cytoskeleton What Are Its Functions Quora